
 Home Home |
 For authors For authors |
 Submission status Submission status |
 Current Current
|
 Archive Archive
|
 Archive
(English) Archive
(English)
|
 Search Search |
The interplay between nontrivial band structure and magnetic order in topological insulators is a rich source of remarkable quantum phenomena such as quantum anomalous Hall effect, axion electrodynamics, Majorana fermions, etc. These phenomena are manifested through topologically protected electron states appearing at the sample boundaries. A qualitatively new stage of investigations in this topic is triggered by the discovery of materials that combine topological properties with intrinsic antiferromagnetic order.
In this letter we present a theoretical investigation of modification of low-energy surface electron structure caused by the noncollinear magnetic domain walls in intrinsic antiferromagnetic topological insulator. The study is carried out on the basis of the Hamiltonian for quasirelativistic fermions by using a continual approach and tight-binding calculations. A bound one-dimensional state is shown to appear at the domain wall, in addition to the surface exchange gap modulation and the shift of a two-dimensional Dirac cone in momentum space. We describe the main characteristics of the bound state such as the energy spectrum (see the figure), spatial localization and spin polarization depending on orientation of domain magnetizations.
We consider possibilities of experimental observation of the bound states associated with the noncollinear magnetic domain walls and their contribution to quantum effects on the (0001) surface of the antiferromagnetic topological insulators of the MnBi2Te4 -type.
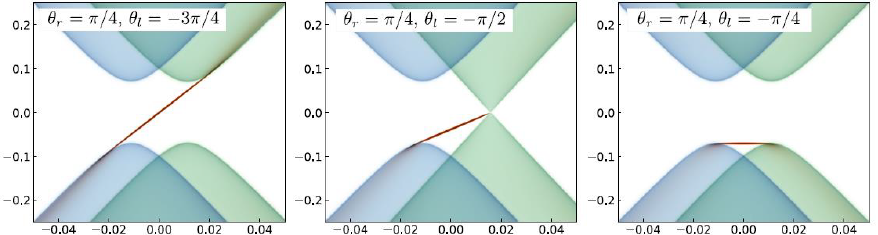
Spectral dependencies of the one-dimensional bound state (red color) induced by magnetic wall and projection of the Dirac cone two-dimensional states for different orientations of the domain magnetizations.
V. N. Men’shov, I. P. Rusinov, E. V. Chulkov
JETP Letters 114, issue 11 (2021)