
 Home Home |
 For authors For authors |
 Submission status Submission status |
 Current Current
|
 Archive Archive
|
 Archive
(English) Archive
(English)
|
 Search Search |
The ability to explain when and why an isolated quantum mechanical system can be accurately described with equilibrium statistical mechanics is one of the key challenges in modern statistical physics. Such description may be possible even for time-dependent Hamiltonians, and much attention has focused on the emergence of quasi-equilibrium states in many-particle periodically driven systems. Numerous approximate methods have been developed to describe dynamics of such systems, known as Floquet dynamics. Interesting results were previously obtained when the external driving frequency significantly exceeds the strength of the interaction in the system in frequency units (the averaging condition).
NMR in solids was one of the first areas where experimental and theoretical investigations of dynamics and thermodynamics in periodically driven systems were performed. The powerful experimental technique of NMR and relatively simple analytic tools allowed the creation of “spin alchemy” with very interesting results.
In this letter we work out a numerical method to investigate Floquet dynamics in the simplest multi-pulse NMR experiment in a system of 14 spins connected by dipole-dipole interactions. We discover that a quasi-thermodynamic equilibrium is established under the averaging condition. When this condition is not met, instead of a quasi-equilibrium state, we find that the polarization decays to zero.
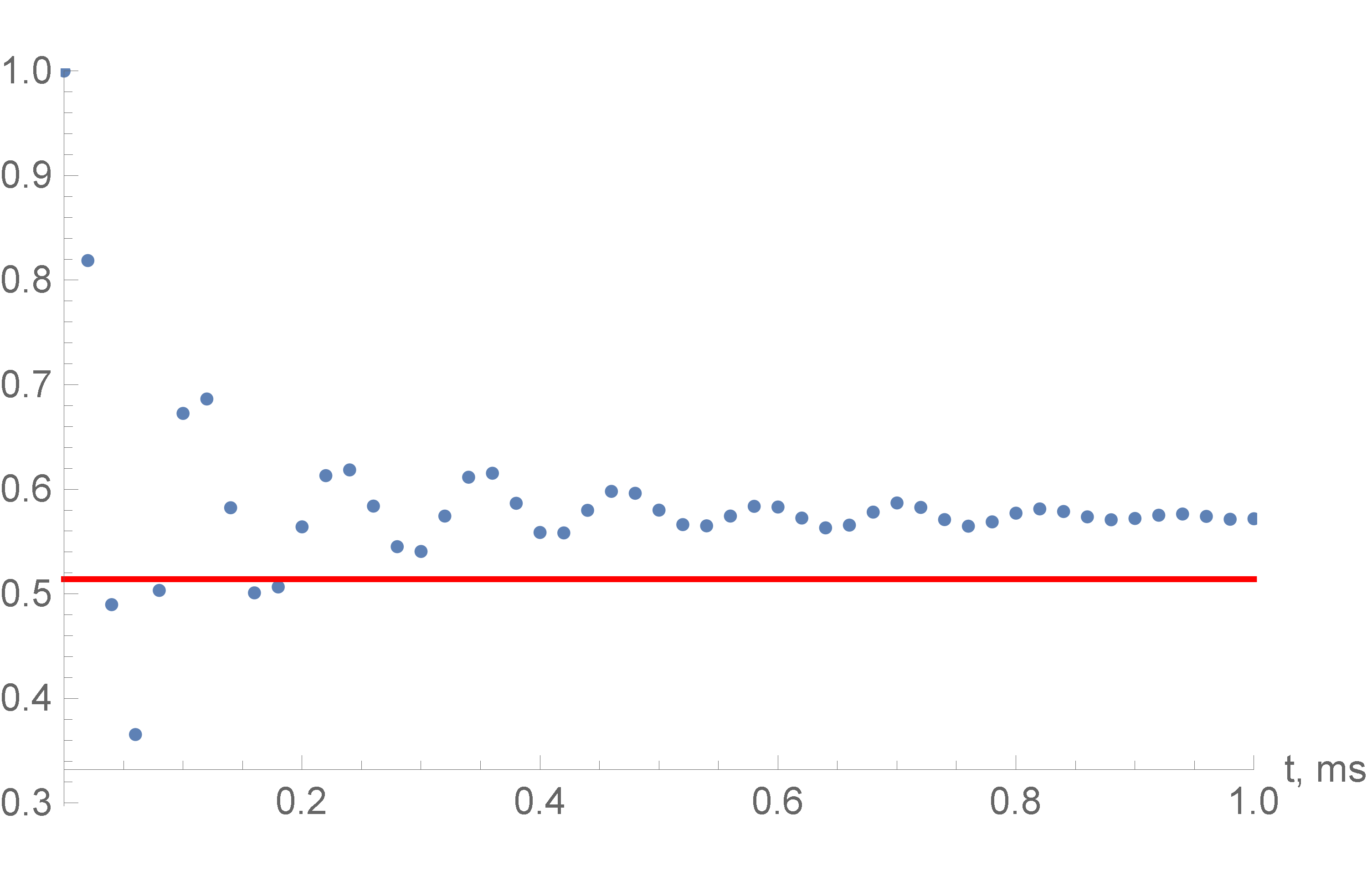
The decay of the polarization in multi-pulse NMR spin-locking with π/8 RF pulses. The initial polarization equals 1. The horizontal line is the thermodynamic equilibrium polarization.The number of the spins is 14. The averaging condition is satisfied.
G.A.Bochkin, S.G.Vasil’ev, A.V.Fedorova, E.B.Fel’dman
JETP Letters 112, issue 11 (2020)