
 Home Home |
 For authors For authors |
 Submission status Submission status |
 Current Current
|
 Archive Archive
|
 Archive
(English) Archive
(English)
|
 Search Search |
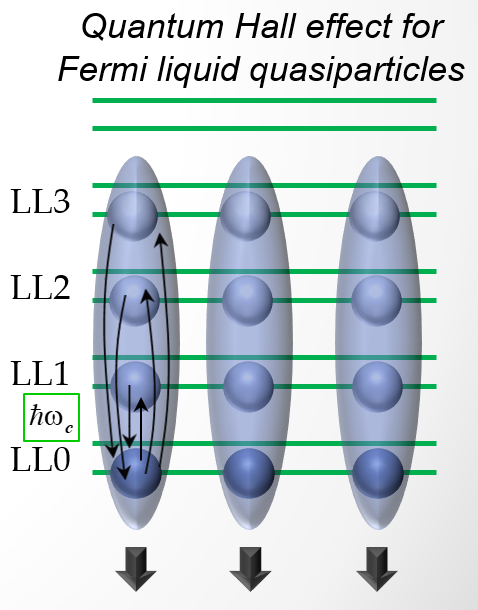
A review is given of unusual many-particle effects discovered in strongly interacting two-dimensional electronic systems in quantizing magnetic fields in MgZnO/ZnO heterostructures. The studied two-dimensional systems have unique properties - strong Coulomb interaction, characterized by the high values of the Wigner-Seits parameter rs~5-10 and, at the same time, high low-temperature mobilities, which enable detecting numerous many-particle effects. The properties of collective electronic excitations in the regime of the integer quantum Hall effect are investigated by the method of inelastic light scattering. Many results concerning both the structure of the ground state and many-particle contributions to the energy of collective excitations go far beyond the well-known concepts of the microscopic structure of quantum Hall states. Despite the absence of a rigorous theory of 2D electron systems for rs>>1, the observed effects can be described in terms of Fermi-liquid quasiparticles with renormalized parameters. The phenomena of renormalization of the quasiparticle effective mass, its spin susceptibility, ferromagnetic instabilities at even filling factors, as well as the strongest renormalization of their exchange interaction are studied experimentally. The observed effects are quantitatively described by calculations performed using the method of exact diagonalization of the energy spectrum, which takes into account the Coulomb mixing of Landau levels . The results of the analysis allow to reveal the characteristics of Fermi-liquid quasiparticles, smeared across multiple Landau levels and to probe their Hall quantization (see the figure).
A.B. Vankov and I.V. Kukushkin
JETP Letters 113, issue 2 (2021)