
 Home Home |
 For authors For authors |
 Submission status Submission status |
 Current Current
|
 Archive Archive
|
 Archive
(English) Archive
(English)
|
 Search Search |
After the discovery of Mott insulating states and superconductivity in the so-called magic angle twisted bilayer graphene in 2018, the study of this material became a hot topic in condensed matter physics. In single-particle approximation, the system under study has four almost flat almost degenerate bands near the Fermi level. The electron-electron interaction lifts this degeneracy stabilizing some order parameter in the system. The mottness of the ground state of the magic angle twisted bilayer graphene manifests itself in the sequence of conductivity minima observed for several doping levels.
The nature of the ground state of the magic angle twisted bilayer graphene is not yet known. Here, we assume that the emerging non-superconducting order parameter is a spin density wave, and study the evolution of such ordered state with doping. We show that in the range of electron densities, where the order parameter is nonzero, the homogeneous state of the system can be unstable with respect to the phase separation. Phases in the inhomogeneous state are characterized by an even number (n = 0, ±2, ±4) of electrons per a superlattice cell. This allows us to explain some features in the behavior of the conductivity of the system with doping. Thus, we are able to explain the fact that the conductivity minima, that could occur at doping levels corresponding to an odd number (n = ±1, ±3) of electrons per supercell, are absent in some samples under study (phase separation occurs) and are present in other samples (phase separation is suppressed by the long-range Coulomb repulsion).
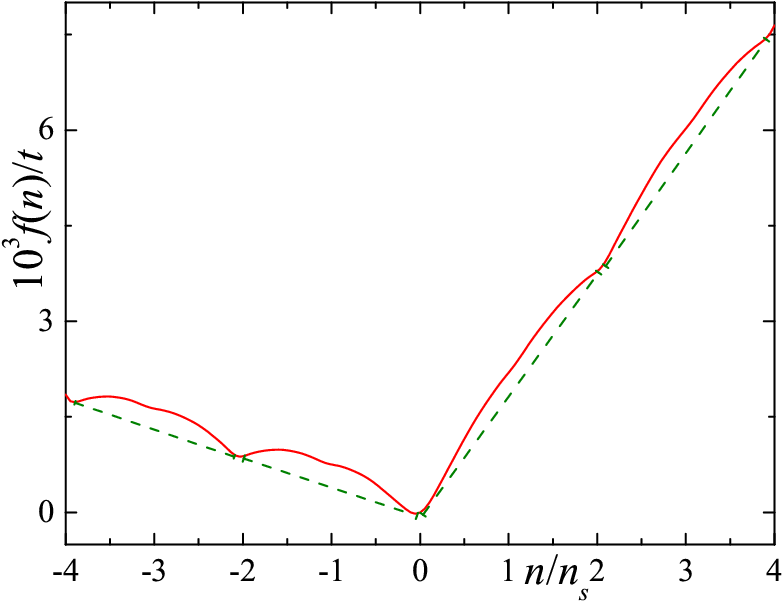
Free energy of the system as a function of doping. The solid (red) curve corresponds to the free energy of the homogeneous state. The energies of the inhomogeneous states obtained by the Maxwell construction are shown by dashed (green) lines
A.O. Sboychakov, A.V. Rozhkov, K.I. Kugel, and A.L. Rakhmanov
JETP Letters 112, issue 10 (2020)