
| VOLUME 77 (2003) | ISSUE 3 | PAGE 162 |
|---|
|
Unconventional magnetoresistance in long InSb nanowires
S. V. Zaitsev-Zotov, Yu. A. Kumzerov*, Yu. A. Firsov*, and P. Monceau+
Institute of Radioengineering and Electronics RAS, 101999 Moscow, Russia *A.F. Ioffe Physical-Technical Institute RAS, 194021 Sankt-Petersburg, Russia +Centre de Recherches sur Les Très Basses Températures, 38042 Grenoble Cédex 9, France ID: 73.23.-b, 73.63.-b
Abstract
Magnetoresistance in long correlated nanowires of degenerate semiconductor InSb in asbestos matrix (wire diameter of around 5 nm, length 0.1-1 mm) is studied over temperature range 2.3-300 K. At zero magnetic field the electric conduction G and the current-voltage characteristics of such wires obey the power laws 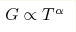 , , 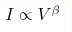 , expected for
one-dimensional electron systems. The effect of magnetic field corresponds
to a 20% growth of the exponents α, β at H=10 T. The
observed magnetoresistance is caused by the magnetic-field-induced breaking of
the spin-charge separation and represents a novel mechanism of
magnetoresistance. , expected for
one-dimensional electron systems. The effect of magnetic field corresponds
to a 20% growth of the exponents α, β at H=10 T. The
observed magnetoresistance is caused by the magnetic-field-induced breaking of
the spin-charge separation and represents a novel mechanism of
magnetoresistance.
|
 Home
Home