
| VOLUME 101 (2015) | ISSUE 7 | PAGE 512 |
|---|
|
Anomalous Hall effect in MnSi: intrinsic to extrinsic crossover
V. V. Glushkov+*, I. I. Lobanova+*, V. Yu. Ivanov+, S. V. Demishev+*
+Prokhorov General Physics Institute of the RAS, 119991 Moscow, Russia *Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, 141700 Dolgoprudny, Russia
Abstract
Temperature dependences of low field Hall resistivity ρH are used to separate anomalous (ρHa) and normal (RHB) contributions to Hall effect in chiral magnet MnSi ( 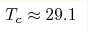 K). It is found that the transition
between paramagnetic (T>Tc) and magnetically ordered (T<Tc) phases
is accompanied by the change in anomalous Hall resistivity from low temperature
behavior governed by Berry phase effects
(ρHa=μ0S2ρ2M,
T<Tc) to high temperature regime dominated by skew scattering
(ρHa=μ0S1ρ M, T>Tc). The crossover between the
intrinsic ( K). It is found that the transition
between paramagnetic (T>Tc) and magnetically ordered (T<Tc) phases
is accompanied by the change in anomalous Hall resistivity from low temperature
behavior governed by Berry phase effects
(ρHa=μ0S2ρ2M,
T<Tc) to high temperature regime dominated by skew scattering
(ρHa=μ0S1ρ M, T>Tc). The crossover between the
intrinsic (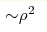 ) and extrinsic ( ) and extrinsic (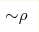 ) contributions to
anomalous Hall effect develops together with the noticeable increase of the
charge carriers' concentration estimated from the normal Hall coefficient (from
n/nMn( ) contributions to
anomalous Hall effect develops together with the noticeable increase of the
charge carriers' concentration estimated from the normal Hall coefficient (from
n/nMn(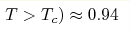 to n/nMn( to n/nMn(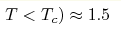 , ,
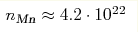 cm-3). The observed features may
correspond to the dramatic change in Fermi surface topology induced by the onset
of long range magnetic order in MnSi. cm-3). The observed features may
correspond to the dramatic change in Fermi surface topology induced by the onset
of long range magnetic order in MnSi.
|
 Home
Home