
| VOLUME 101 (2015) | ISSUE 7 | PAGE 518 |
|---|
|
Thermoelectric properties of Au-based metallic glass at low temperatures
V. V. Pryadun+, D. V. Louzguine-Luzgin*, L. V. Shvanskaya+×, A. N. Vasiliev+×°
+MSU, 119991 Moscow, Russia *WPI Advanced Institute for Materials Research, Tohoku University, Katahira 2-1-1, Aoba-Ku, 980-8577 Sendai, Japan ×National University of Science and Technology "MISiS", 119049 Moscow, Russia °Theoretical Physics and Applied Mathematics Department, Ural Federal University, 620002 Ekaterinburg, Russia
Abstract
Thermoelectric properties of Au49Cu26.9Ag5.5Pd2.3Si16.3 glassy alloy have been studied using electrical resistivity, thermal conductivity and Seebeck coefficient measurements over temperature range 2-390 K. At heating, resistivity ρ decreases in a power-law manner from residual value 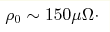 cm.
The temperature coefficient of resistivity, cm.
The temperature coefficient of resistivity,
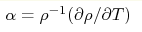 , is rather small and varies
non-monotonously. Thermal conductivity κ rises
linearly at low temperatures; it exhibits a plateau-like feature and sharply
increases at elevated temperatures. Seebeck coefficient S increases with
temperature and exhibits a characteristic "knee" feature. At elevated
temperatures, S increases linearly with
temperature but with a different slope. It total, thermoelectric properties of
Au-based glassy alloy demonstrate behaviour of a highly disordered system in a
most pronounced manner. , is rather small and varies
non-monotonously. Thermal conductivity κ rises
linearly at low temperatures; it exhibits a plateau-like feature and sharply
increases at elevated temperatures. Seebeck coefficient S increases with
temperature and exhibits a characteristic "knee" feature. At elevated
temperatures, S increases linearly with
temperature but with a different slope. It total, thermoelectric properties of
Au-based glassy alloy demonstrate behaviour of a highly disordered system in a
most pronounced manner.
|
 Home
Home