
| VOLUME 103 (2016) | ISSUE 5 | PAGE 365 |
|---|
|
Effect of magnetic field on the intermediate phase in Mn1-xFexSi: spin-liquid vs. fluctuations scenario
S. V. Demisheva,b, I. I. Lobanovaa,b, A. V. Bogacha, V. V. Glushkova,b, V. Yu. Ivanova, T. V. Ischenkoa, N. A. Samarina, N. E. Sluchankoa, S. Gabanic, E. Cizmárd, K. Flachbartc, N. M. Chubovae, V. A. Dyadkine,f, S. V. Grigorieve
aProkhorov General Physics Institute of RAS, 119991 Moscow, Russia bMoscow Institute of Physics and Technology, 141700 Dolgoprudny, Russia cInstitute of Experimental Physics SAS, 040 01 Kosice, Slovak Republic dP.J. Safárik Univesity in Kosice, SK-04001 Kosice, Slovak Republic ePetersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, 188300 Gatchina, Russia fSwiss-Norwegian Beamlines at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, 38000 Grenoble, France
Abstract
We report results of the magnetic field influence on the chiral spin liquid state in Mn1-xFexSi single crystal with iron content x=0.108 in proximity of a hidden quantum critical point. The use of small angle neutron scattering data together with magnetic susceptibility measurements down to 0.4 K and precise magnetoresistance measurements in the temperature range 2-20 K in magnetic field up to 5 T allowed us to construct the magnetic phase diagram of this compound in which at low magnetic fields B<0.15 T an intermediate phase with short-range magnetic order exists in a wide temperature range 0.62<T<9.1 K. It was found that the increase of magnetic field first results in a suppression of transition into spiral phase with long-range magnetic order at very low temperatures, and then induces a transition of the intermediate phase into a spin-polarized (ferromagnetic) phase with lowering temperature. The temperature of this transition TSP increases with magnetic field logarithmically, 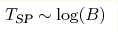 , and results in formation of a singular point on the
magnetic phase diagram located at T , and results in formation of a singular point on the
magnetic phase diagram located at T 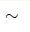 8.5 K and B 8.5 K and B 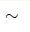 3.5 T,
which may be either a triple or a critical point. The possible spin-liquid
nature of the intermediate phase is discussed. 3.5 T,
which may be either a triple or a critical point. The possible spin-liquid
nature of the intermediate phase is discussed.
|
 Home
Home