
| VOLUME 77 (2003) | ISSUE 12 | PAGE 769 |
|---|
|
Vacuum energy and Universe in special relativity
G. E. Volovik
Low Temperature Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, FIN-02015 HUT, Finland L. D. Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, 117334 Moscow, Russia ID: 03.30.+p, 04.90.+e, 98.80.-k
Abstract
The problem of cosmological constant and vacuum energy is usually thought of as the subject of general relativity. However, the vacuum energy is important for the Universe even in the absence of gravity, i.e. in the case when the Newton constant G is exactly zero, G=0. We discuss the response of the vacuum energy to the perturbations of the quantum vacuum in special relativity, and find that as in general relativity the vacuum energy density is on the order of the energy density of matter. In general relativity, the dependence of the vacuum energy on the equation of state of matter does not contain G, and thus is valid in the limit 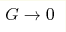 . However, the result obtained for the
vacuum energy in the world without gravity, i.e. when G=0
exactly, is different. . However, the result obtained for the
vacuum energy in the world without gravity, i.e. when G=0
exactly, is different.
|
 Home
Home