
| VOLUME 75 (2002) | ISSUE 8 | PAGE 479 |
|---|
|
Raman spectra of MgB2 at high pressure and topological electronic transition
K. P. Meletov, M. P. Kulakov, N. N. Kolesnikov, J. Arvanitidis+, G. A. Kourouklis+ Institute of Solid State Physics RAS, 142432 Chernogolovka, Moscow reg., Russia +Physics Division, School of Technology, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, GR-540 06 Thessaloniki, Greece ID: 74.62.Fj, 74.25.Kc, 74.25.Gz
Abstract
Raman spectra of the MgB2 ceramic samples were measured as a function of pressure up to 32 GPa at room temperature. The spectrum at normal conditions contains a very broad peak at 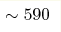 cm-1 related
to the E2g phonon mode. The frequency of this mode exhibits a strong
linear dependence in the pressure region from 5 to 18 GPa, whereas beyond
this region the slope of the pressure-induced frequency shift is reduced by
about a factor of two. The pressure dependence of the phonon mode up to cm-1 related
to the E2g phonon mode. The frequency of this mode exhibits a strong
linear dependence in the pressure region from 5 to 18 GPa, whereas beyond
this region the slope of the pressure-induced frequency shift is reduced by
about a factor of two. The pressure dependence of the phonon mode up to
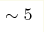 GPa exhibits a change in the slope as well as a "hysteresis"
effect in the frequency vs. pressure behavior. These singularities in the
E2g mode behavior under pressure support the suggestion that MgB2 may
undergo a pressure-induced topological electronic transition. GPa exhibits a change in the slope as well as a "hysteresis"
effect in the frequency vs. pressure behavior. These singularities in the
E2g mode behavior under pressure support the suggestion that MgB2 may
undergo a pressure-induced topological electronic transition.
|
 Home
Home