
| VOLUME 73 (2001) | ISSUE 4 | PAGE 196 |
|---|
|
Ion H2+ can dissociate in a strong magnetic field
A. V. Turbiner*, J.-C. López+, A. Flores-Riveros
 *Laboratoire de Physique Theorique, Universite Paris-Sud, Orsay F-91405 France and Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, UNAM, México +Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, UNAM, Apartado Postal 70-543, 04510 México D.F., México  Instituto de Física, Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla Instituto de Física, Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla Apartado Postal J-48, Puebla Pue. 72570, México ID: 31.10.+z, 31.15.Pf, 32.60.+i, 97.10.Ld
Abstract
In framework of a variational method the molecular ion H2+ in a magnetic field is studied. An optimal form of the vector potential corresponding to a given magnetic field (gauge fixing) is chosen variationally. It is shown that for any magnetic field strength as well as for any orientation of the molecular axis the system (ppe) possesses a minimum in the potential energy. The stable configuration always corresponds to elongation along the magnetic line. However, for magnetic fields 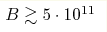 G
and some orientations the ion H2+ becomes unstable decaying to
H-atom + p. G
and some orientations the ion H2+ becomes unstable decaying to
H-atom + p.
|
 Home
Home