
| VOLUME 82 (2005) | ISSUE 4 | PAGE 234 |
|---|
|
Hall coefficient in heavy fermion metals
V. R. Shaginyan, K. G. Popov+, S. A. Artamonov
Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, RAS, 188300 Gatchina, Russia +Komi Science Center, Ural Division, RAS, 167982 Syktyvkar, Russia ID: 71.10.Hf, 71.27.+a, 74.72.-h
Abstract
Experimental studies of the antiferromagnetic (AF) heavy fermion metal YbRh2Si2 in a magnetic field B indicate the presence of a jump in the Hall coefficient at a magnetic-field tuned quantum state in the zero temperature limit. This quantum state occurs at 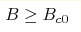 and
induces the jump even though the change of the magnetic field at B=Bc0
is infinitesimal. We investigate this by using the model of heavy electron
liquid with the fermion condensate. Within this model the jump takes place
when the magnetic field reaches the critical value Bc0 at which the
ordering temperature TN(B=Bc0) of the AF transition vanishes. We show
that at B→ Bc0, this second order AF phase transition becomes the
first order one, making the corresponding quantum and thermal critical
fluctuations vanish at the jump. At T→0 and B=Bc0, the Grüneisen
ratio as a function of temperature T diverges. We demonstrate that both the
divergence and the jump are determined by the specific low temperature
behavior of the entropy and
induces the jump even though the change of the magnetic field at B=Bc0
is infinitesimal. We investigate this by using the model of heavy electron
liquid with the fermion condensate. Within this model the jump takes place
when the magnetic field reaches the critical value Bc0 at which the
ordering temperature TN(B=Bc0) of the AF transition vanishes. We show
that at B→ Bc0, this second order AF phase transition becomes the
first order one, making the corresponding quantum and thermal critical
fluctuations vanish at the jump. At T→0 and B=Bc0, the Grüneisen
ratio as a function of temperature T diverges. We demonstrate that both the
divergence and the jump are determined by the specific low temperature
behavior of the entropy 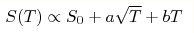 with S0, a and
b are temperature independent constants. with S0, a and
b are temperature independent constants.
|
 Home
Home